Basic Instrumentation fundamentals
Here we are for knowing about what is basically instrumentation. Automation related all helpful topics are included with Diagram
Introduction :-It is branch of engineering which deals with the measurement monitoring display and plant control operation.
Normally basic instrumentation question and answer ask by interviewer in interview, but you should knowledge about basic instrumentation behavior and working conditions.
INSTRUMENT
Instrument is device. which is used for measure, monitor , display etc. of a process Variables.
so question is what is process variables .
Process variables are:- Flow, Pressure, Temperature, Level and Quality.
Here quality stands for (%,O2,Co2,Ph etc)
Here quality stands for (%,O2,Co2,Ph etc)
Question-1-How to define all the process variables and state there unit of measurement ?
Answer-1- As we know about process variables are :-
- Flow
- Pressure
- Temperature
- Level
- Quality.
Now we know about what is the definition of all variables.
Flow:- Volume per unit of time at specified temperature and pressure.
Condition,is generally measurement by positive
displacement or rate meters.
Units:kg/hr,Liter/min,gallon/min,m3/hr, Nm3/hr.
Pressure :- Force acting per unit Area P=F/A
Unit:- Bar, kg/cm2, Pascal, mpa, kpa, LB/in2
Level:- Different Between two heights.
Unit:- Meter, mm , cm, % .
Temperature:- it is the degree of Hotness or Coldness of a Body.
Unit:- °C ,°K,°R ,°F
Quality :- it is deals with analysis.
Unit:- pH, % , CO2. %O2.
Question-2-What are the primary elements used for flow measurement?
Answer-2-The primary elements used for flow measurement are:
- Orifice Plate
- Venturi tube
- Pitot tube.
- Annubars.
- Flow Nozzle.
- Weir & Flumes.
Question-3- What are the different types of orifice plates and state their uses?
Answer-3-The different types of orifice plates are:
- Concentric.
- Segmental.
- Eccentric.
- Quadrant Edge.
Concentric: The concentric orifice plate is used for ideal liquid as well as gases and steam service. This orifice plate beta ratio falls between of 0.15 to 0.75 for liquids and 0.20 to 0.70 for gases and steam. Best results occur between value of 0.4 and 0.6, beta ratio means ratio of the orifice bore to the internal pipe diameters.
Eccentric:-The eccentric orifice plate has a hole eccentric. Use full for measuring containing solids, oil containing water and steam. Eccentric plates can use either flange or vena contracta taps, but the tap must be at 180 or 90 to the ec opening. Eccentric orifices have the bore offset from center to Minimize problems in services of solids-containing materials.
fig 2
Segmental: The segmental orifice place has the hole in the form segment of a circle. This is used for colloidal and slurry flow measurement. For best accuracy, the tap location should be 180° from the center of tangency.
fig 3
Quadrant Edge: It common use in Europe and are particularly useful for pipe sizes less than 2 inches. Quadrant edge orifices produce a relatively constant coefficient of discharge for services with low Reynolds numbers in the range from 100,000 down to 5,000.
Question-4- How do you identify an orifice in the pipeline?
Answer-4- An orifice tab is welded on the orifice plate, which extends out of the line
giving an indication of the orifice plate.
Question-5- Why is the orifice tab provided?
Answer-5-The orifice tab is provided due to the following reasons.
Indication of an orifice plate in a line.
- The orifice diameter is marked on it.
- The material of the orifice plate.
- The tag no. of the orifice plate.
- The mark the inlet of an orifice.
Question-6- What is Bernoulli's theorem and where it is applicable?
Answer-6-Theorem states the "total energy of a liquid flowing from
one point to another remain constant."
It is applicable for non-compressible liquids.
Question-7- How do you identify the H. P. side or inlet of an orifice plate in line?
Answer-7-The marking is always done H. P. side of the orifice tab, which gives
an indication of the H. P. side.
Question-8- How do you calibrate a D. P. transmitter?
Answer-8-The following steps are to be taken which calibrating:
1. Adjust zero of the Xmtrs.
2. Static pressure test: Give equal pressure on both sides of the transmitter.
3. Zero should not shift.
4. If it is shifting carry out static alignment.
5. Vacuum test: Apply equal vacuum to both the sides. The zero should not shift.
4. Calibration Procedure:
- Give 20-psi air supply to the transmitter.
- Vent the L.P. side to atmosphere.
- Connect output of the Instrument to a standard test gauge.
- Adjust zero.
5. Apply required pressure to high-pressure side of the transmitter and adjust the span.
6. Adjust zero again if necessary.
Question-9- What is the seal liquid used for filling impulse lines on crude and viscous liquid?
Answer-9- Glycol.
Question 10. How do you carry out piping for a Different pressure flow
transmitter on liquids, Gas and steam services? Why?
Answer-10- Liquid lines: On liquid lines the transmitter is mounted below the orifice plate
because liquids have a property o self-draining.
Gas Service: On gas service the transmitter is mounted above the orifice plane venting and secondly condensate formation.
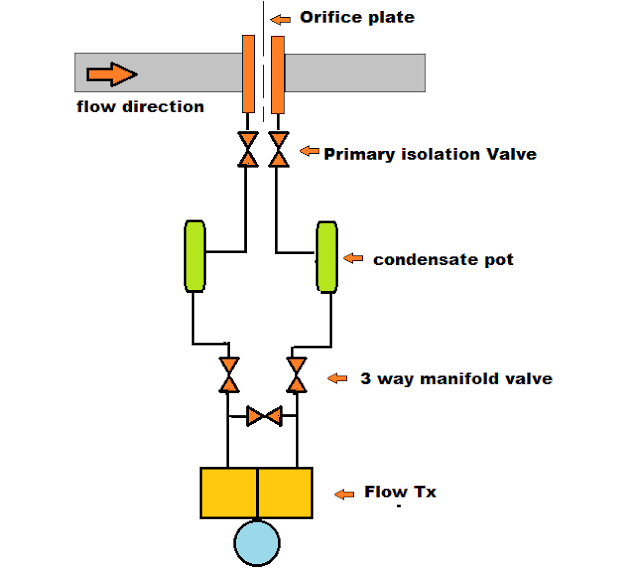
Steam Service: On steam service the transmitter is mounted below the orifice plate with condemate pots. The pots should be at the same level.
Question-11- Draw a flow control Loop.
Answer-11-
Question-12-An technician tells you that flow indication is more?
How would you start checking?
Answer-12- First flushing the transmitter.
- Flush both the impulse lines.
- Adjust the zero by equalizing if necessary.
- If still indication is more then.
- Check LP. side for choke.
- If that is clean then.
- Check the leaks on L.P. side.
- If not.Calibrate the transmitter.
Question-13- How do you do a zero checks on a D.P. transmitter?
Answer-13-Close one of the valve either H.P. or L.P. open the equalizing valve.
The O/P should read zero.
Question-14- How would you do Glycol filling or fill seal liquids in seal pots?
Answer-14- The procedure for glycol filling is:-
- Close the primary isolation valves.
- Open the vent on the seal pots.
- Drain the use glycol if present.
- Connect a hand pump on L.P.
- side while filling the H.P. side with glycol.
- Keep the equalizer valve open.
- Keep the L.P. side valve closed.
- Start pumping and fill glycol. Same repeat for L.P.
- side by connecting pump to H.P. side
- ,keeping equalizer open and H.P.
- side isolation valve closed.
- Close the seal pot vent valves.
- Close equalizer valve.
- Open both the primary isolation valves.
Question-15- How will you vent air in the D.P. cell? What if seal pots are used?
Answer-15-Air is vented by opening the vent plugs on a liquid service transmitter.
On services where seal pots are used isolate the primary isolation valves and
open the vent valves. Fill the line from the transmitter drain plug with a pump.
Question-16-Why flow is measured in square root?
Answer-16- Flow varies directly
as the square root of different pressure F = K
square root of Ap. since this flow varies as the square root of
differential pressure the pen does not directly indicate flow.
the flow can be determined by taking by square root of pen.
Question-17- What is absolute pressure?
Answer-17- Absolute pressure is the total pressure present in the system
Abs. pressure = Gauge pressure + Atm. pressure.
Question-18. What is absolute zero pressure?
Answer-18-Absolute zero = 760 mm Hg Vacuum.
Question-19- What is the maximum Vacuum?
Answer-19-The maximum Vacuum = 760 mm Hg.
Question- 20. What are the primary elements for measuring pressure?
Answer-20-The primary elements used for measuring pressure are:
- Bourdon tube.
- Diaphragm.
- Capsule.
- Bellows.
- Pressure Springs.
The above are known as elastic deformation pressure elements.
- Type of Bourdon tubes.
- 'C'type.
- Spiral.
- Helix.
Diaphragm: The diaphragm is best suited for low-pressure measurement.
Capsules:- Two circular diaphragms are welded together to form a pressure capsule. Material Used phosphor bronze, Ni-spane stainless steel.
Bellows:-Bellows is a one - piece, collapsible, seamless metallic unit with deep folds formed from
very tin walled tubing Material used: Brass, phosphor bronze, and stainless steel.
Used for high Pressure.
Pre. spring: Pressure springs of helical or spiral shape used for measuring high pressures
Question-21- How will you calibrate an absolute pressure transmitter-using vacuum manometer Range 0-400 mm abs?
Answer-21-The procedure for calibration is as follows:
- Connect air supply to the transmitter.
- Connect a test gauge of 0-1.4 Kg/cm2 to the output.
- Connect Vacuum pump with tee off to the manometer.
- Apply 760 mm Vacuum (or nearest) and adjust zero.
- Apply 360 mm Vacuum adjust span. (760 - 360 =400 mm abs.)
.
Question- 22-. What is the principle of a pressure gauge?
Answer-22- Pressure gauge works on Hooks law .
Principle: "Measuring the stress in an elastic medium" .
********************************************************************************
***************
Interview Questions for
Instrumentation Engineering
click link->>>>
https://instquesvtion2020.blogspot.com/2020/06/interview-questions-for-instrumentation.html








Comments
Post a Comment